Cutaneous Candidiasis
People who are diabetic, have suppressed immune systems, patients undergoing antibiotic or chemotherapy treatment and denture wearers are more susceptible to Oral Candidiasis (Oral Thrush). It is particularly important to catch it early in infants and children. Because of the discomfort caused by oral thrush, they may stop eating and/or drinking. Candidal Intertrigo is more common among people who are overweight.
At Dermatology Associates & Surgery Center, our skin experts are here to help you regain your confidence in your skin. With a proper treatment plan, our dermatologists can assist you in managing candidiasis.
Examples of Cutaneous Candidiasis
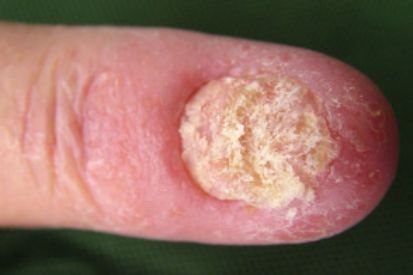
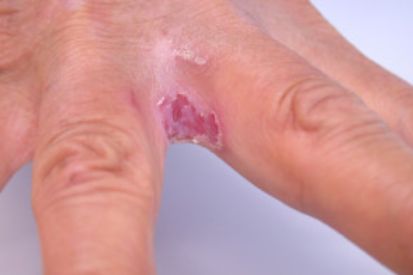
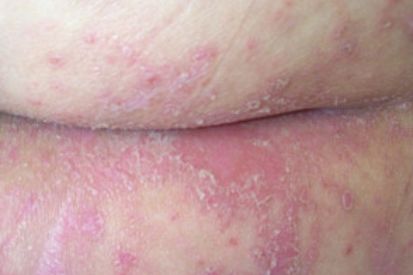
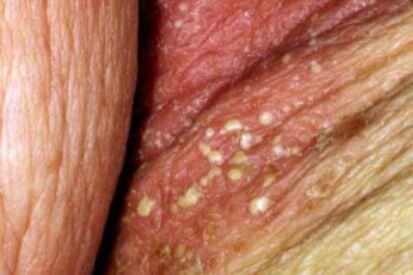
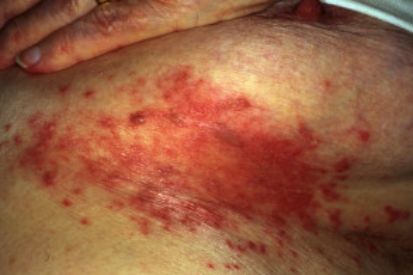
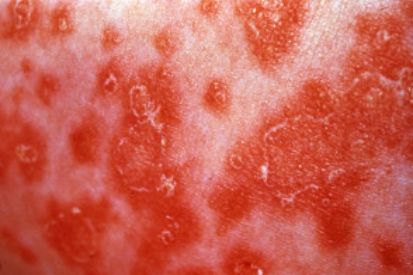
What are the Symptons of Candidiasis?
- Oral Candidiasis (Oral Thrush): Characterized by lacy, white patches on top of reddened areas on the tongue, throat, and mouth. Can include fever, and burning sensation in the mouth.
- Diaper Rash: Some diaper rashes are bacterial, but many are caused by yeast infections.
- Candidal Intertrigo: Ooccurs in moist overlapping skin folds, such as areas in the inner thighs, armpits, and under the breasts. It is characterized by red, raw skin surrounded by scaling and lesions that itch, ooze, or hurt.
Causes of Candidiasis
- Candidiasis is caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus.
- Candida is a type of yeast that naturally resides in various parts of our body, such as the mouth, gut, and genital area.
- Normally, it coexists peacefully with other microorganisms. However, certain factors can disrupt this balance, leading to excessive growth of Candida and triggering an infection.
Candidiasis Prevention
Preventing Candidiasis involves adopting healthy hygiene habits and minimizing factors that contribute to yeast overgrowth. In partnership with your dermatologist, a treatment plan can help you prevent the skin-related forms of candidiasis.
Candidiasis FAQs
A dermatologist can diagnose cutaneous candidiasis through a visual examination of the affected skin. In some cases, a skin scraping or swab may be taken for microscopic examination or culture to confirm the presence of Candida. Proper diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment.
Cutaneous candidiasis is generally not considered contagious in the sense of person-to-person transmission. The yeast that causes the infection, Candida, is a normal part of the skin flora. However, the infection can spread from one area of the body to another, especially if the conditions for yeast growth are favorable. Sharing personal items, such as towels or razors, may contribute to the spread of infection within the same individual.
It's important to practice good personal hygiene and avoid sharing personal items to minimize the risk of developing or spreading cutaneous candidiasis. If you have concerns about your skin or suspect a fungal infection, consulting with your dermatologist can provide personalized guidance and treatment options.
Cutaneous candidiasis is a relatively common fungal infection, and its prevalence can vary depending on several factors such as age, overall health, and environmental conditions.
While cutaneous candidiasis is common, it is generally a manageable condition with appropriate treatment. Topical antifungal medications are often effective in treating localized infections, and oral antifungal medications may be prescribed in more severe or widespread cases.
How to Treat Candidiasis
If you suspect or are diagnosed with candidiasis, consulting a dermatologist is a key step for effective treatment. Dermatologists specialize in fungal infections like candidiasis. Treatment typically involves antifungal medications, which may be in the form of topical creams, ointments, or oral pills, depending on the severity and location of the infection.
To treat diaper rash, use over-the-counter powders and ointments and antifungal creams and lotions. Plan on frequent diaper changes to give the skin a chance to be exposed to air regularly. If diaper rash doesn’t abate in seven to 10 days, contact your dermatologist. Candidal intertrigo is treated with medicated topical creams.
Your dermatologist will assess the extent of the candidiasis and prescribe the appropriate medication. Topical treatments are often sufficient for mild cases, targeting the affected area directly. Oral medications may be recommended for more severe or systemic infections.
In addition to medications, your dermatologist may offer guidance on optimal skincare practices to complement the treatment. Your skin is our top priority. Schedule today.
Featured Products

EltaMD UV Physical SPF 41
For oil-free sun protection with just a touch of color, EltaMD's lightly tinted UV Physical is a healthy choice. This chemical-free mineral sunscreen has antioxidants to neutralize free radicals. Water-resistant UV Physical withstands water, humidity and perspiration. 3 oz

EltaMD UV Sheer Broad-Spectrum SPF 50
UV Sheer has a lightweight, hydrating formula that feels silky to the touch and light and airy on the skin. It goes on smooth absorbing quickly into skin and helps even out skin tone. This facial sunscreen offers up to 80 minutes of sweat and water-resistance making it the ideal choice for an active lifestyle, hot and humid weather and for anyone looking for a lightweight and hydrating sunscreen to live freely under the sun. UV Sheer is formulated to be compatible on all skin tones without leaving a white cast. 3.0 oz
